有偿问答
面经分享
技术探讨
资料领取
登录
教你优雅的实现 SpringBoot 并行任务
社长
1年前
⋅ 1879 阅读
Spring Boot 的定时任务: ### 第一种:把参数配置到.properties文件中: ### 代码: ``` package com.accord.task; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.util.Date; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /** * 从配置文件加载任务信息 * @author 王久印 */ @Component public class ScheduledTask { private static final SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss"); //@Scheduled(fixedDelayString = "${jobs.fixedDelay}") @Scheduled(fixedDelayString = "2000") public void getTask1() { System.out.println("任务1,从配置文件加载任务信息,当前时间:" + dateFormat.format(new Date())); } @Scheduled(cron = "${jobs.cron}") public void getTask2() { System.out.println("任务2,从配置文件加载任务信息,当前时间:" + dateFormat.format(new Date())); } } ``` application.properties文件: ``` jobs.fixedDelay=5000 jobs.cron=0/5 * * * * ? ``` SpringBootCron2Application.java中: ``` package com.accord; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableScheduling; @SpringBootApplication @EnableScheduling public class SpringBootCron2Application { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringBootCron2Application.class, args); } } ``` > 注:@EnableScheduling 这个一定要加上;否则,不会定时启动任务! @Scheduled中的参数说明: * `@Scheduled(fixedRate=2000)`:上一次开始执行时间点后2秒再次执行; * `@Scheduled(fixedDelay=2000)`:上一次执行完毕时间点后2秒再次执行; * `@Scheduled(initialDelay=1000, fixedDelay=2000)`:第一次延迟1秒执行,然后在上一次执行完毕时间点后2秒再次执行; * `@Scheduled(cron="* * * * * ?")`:按cron规则执行。 在线Cron表达式生成器:`http://cron.qqe2.com/` ### 第二种定时任务:单线程和多线程 ### #### 1、创建定时任务: #### ``` package com.accord.task; import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /** * 构建执行定时任务 * @author 王久印 * TODO */ @Component public class ScheduledTask2 { private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ScheduledTask2.class); private int fixedDelayCount = 1; private int fixedRateCount = 1; private int initialDelayCount = 1; private int cronCount = 1; @Scheduled(fixedDelay = 5000) //fixedDelay = 5000表示当前方法执行完毕5000ms后,Spring scheduling会再次调用该方法 public void testFixDelay() { logger.info("===fixedDelay: 第{}次执行方法", fixedDelayCount++); } @Scheduled(fixedRate = 5000) //fixedRate = 5000表示当前方法开始执行5000ms后,Spring scheduling会再次调用该方法 public void testFixedRate() { logger.info("===fixedRate: 第{}次执行方法", fixedRateCount++); } @Scheduled(initialDelay = 1000, fixedRate = 5000) //initialDelay = 1000表示延迟1000ms执行第一次任务 public void testInitialDelay() { logger.info("===initialDelay: 第{}次执行方法", initialDelayCount++); } @Scheduled(cron = "0 0/1 * * * ?") //cron接受cron表达式,根据cron表达式确定定时规则 public void testCron() { logger.info("===initialDelay: 第{}次执行方法", cronCount++); } } ``` 使用 @Scheduled来创建定时任务 这个注解用来标注一个定时任务方法。 通过看 @Scheduled源码可以看出它支持多种参数: * cron:cron表达式,指定任务在特定时间执行; * fixedDelay:表示上一次任务执行完成后多久再次执行,参数类型为long,单位ms; * fixedDelayString:与fixedDelay含义一样,只是参数类型变为String; * fixedRate:表示按一定的频率执行任务,参数类型为long,单位ms; * fixedRateString: 与fixedRate的含义一样,只是将参数类型变为String; * initialDelay:表示延迟多久再第一次执行任务,参数类型为long,单位ms; * initialDelayString:与initialDelay的含义一样,只是将参数类型变为String; * zone:时区,默认为当前时区,一般没有用到。 * #### 2、开启定时任务: #### ``` package com.accord; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableScheduling; @SpringBootApplication @EnableScheduling public class SpringBootCron2Application { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringBootCron2Application.class, args); } } ``` > 注:这里的 @EnableScheduling 注解,它的作用是发现注解 @Scheduled的任务并由后台执行。没有它的话将无法执行定时任务。 引用官方文档原文: > @EnableScheduling ensures that a background task executor is created. Without it, nothing gets scheduled. #### 3、执行结果(单线程) #### 就完成了一个简单的定时任务模型,下面执行springBoot观察执行结果: 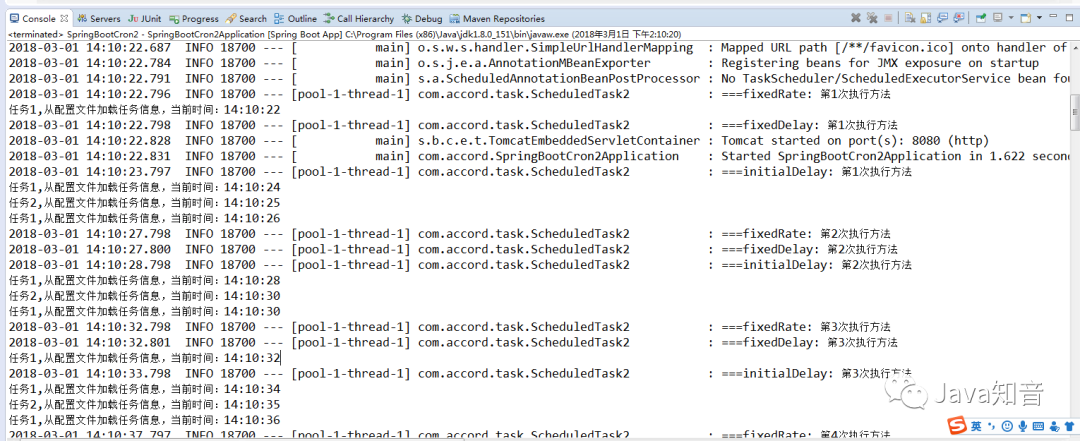 从控制台输入的结果中我们可以看出所有的定时任务都是在同一个线程池用同一个线程来处理的,那么我们如何来并发的处理各定时任务呢,请继续向下看。 #### 4、多线程处理定时任务: #### 看到控制台输出的结果,所有的定时任务都是通过一个线程来处理的,我估计是在定时任务的配置中设定了一个`SingleThreadScheduledExecutor`,于是我看了源码,从`ScheduledAnnotationBeanPostProcessor`类开始一路找下去。果然,在`ScheduledTaskRegistrar`(定时任务注册类)中的`ScheduleTasks`中又这样一段判断: ``` if (this.taskScheduler == null) { this.localExecutor = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor(); this.taskScheduler = new ConcurrentTaskScheduler(this.localExecutor); } ``` 这就说明如果`taskScheduler`为空,那么就给定时任务做了一个单线程的线程池,正好在这个类中还有一个设置`taskScheduler`的方法: ``` public void setScheduler(Object scheduler) { Assert.notNull(scheduler, "Scheduler object must not be null"); if (scheduler instanceof TaskScheduler) { this.taskScheduler = (TaskScheduler) scheduler; } else if (scheduler instanceof ScheduledExecutorService) { this.taskScheduler = new ConcurrentTaskScheduler(((ScheduledExecutorService) scheduler)); } else { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unsupported scheduler type: " + scheduler.getClass()); } } ``` 这样问题就很简单了,我们只需用调用这个方法显式的设置一个`ScheduledExecutorService`就可以达到并发的效果了。我们要做的仅仅是实现`SchedulingConfigurer`接口,重写`configureTasks`方法就OK了; ``` package com.accord.task; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.SchedulingConfigurer; import org.springframework.scheduling.config.ScheduledTaskRegistrar; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; /** * 多线程执行定时任务 * @author 王久印 */ @Configuration //所有的定时任务都放在一个线程池中,定时任务启动时使用不同都线程。 public class ScheduleConfig implements SchedulingConfigurer { @Override public void configureTasks(ScheduledTaskRegistrar taskRegistrar) { //设定一个长度10的定时任务线程池 taskRegistrar.setScheduler(Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(10)); } } ``` #### 5、执行结果(并发) #### 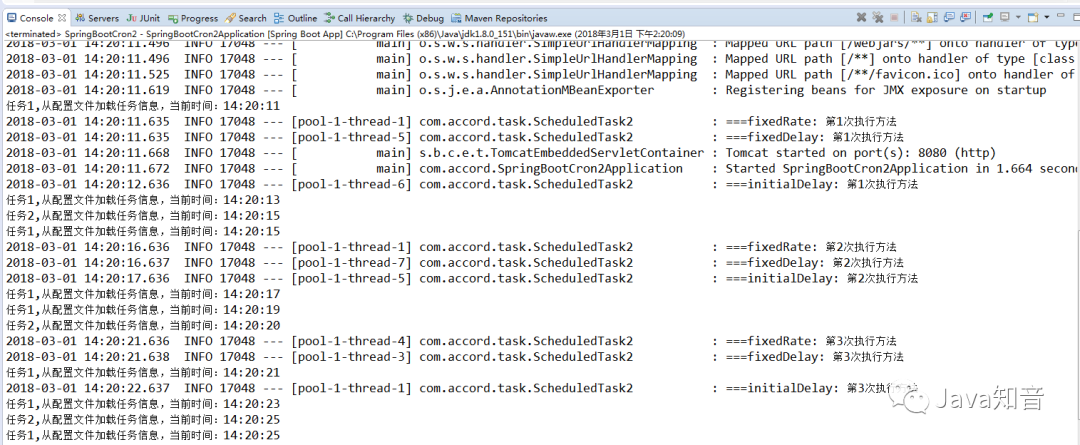 通过控制台输出的结果看出每个定时任务都是在通过不同的线程来处理了。 *来源:wangjiuyin.blog.csdn.net/article/details/79411952* **推荐** [Java面试题宝典](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/jGEkHTf2X8l-wUenc-PpEw) [技术内卷群,一起来学习!!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/jGEkHTf2X8l-wUenc-PpEw)  PS:因为公众号平台更改了推送规则,如果不想错过内容,记得读完点一下**“在看”**,加个**“星标”**,这样每次新文章推送才会第一时间出现在你的订阅列表里。点**“在看”**支持我们吧!
阅读全部
全部评论:
0
条
我有话说:
@
发送
-- 目录 --
关注官方公众号:
Java问答社
接收最新有赏问答推送!
最新发布
1.
SpringBoot 接口数据加解密技巧,so easy!
2.
一个依赖搞定 Spring Boot 反爬虫,防止接口盗刷!
3.
Java8 Stream 极大简化了代码,它是如何实现的?
4.
马上大四了,秋招还是春招好?先找工作还是找实习?
5.
万字详解 Linux 常用指令(值得收藏)
6.
4年工作经验,多线程间的5种通信方式都说不出来,你敢信?
最新评论
部署文档没有了,您能提供下吗
部署文档没有了,能提供下吗
我测你的🐎
源码从哪里获取请问
想学
那篇石墨文档 没有权限查看哇